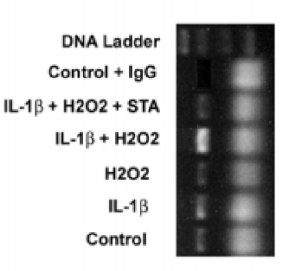
New evidence suggests a retracted paper was felled not by intentional manipulation — as it first appeared — but by a software glitch.
In 2014, we reported that Biochemical Journal had retracted a paper on suspicion it contained “shoddy Photoshopping” — someone appeared to have blacked out a control lane in one figure. Now there’s evidence that it wasn’t done on purpose: An investigation at Duke into eight papers, including the Biochemical Journal paper, did not find evidence of misconduct; lead author Paul Kuo, currently chair of surgery at Loyola Medicine, told us that a glitch in the software caused the black box. Nevertheless, the journal does not plan to un-retract the paper. Continue reading Software glitch — not intentional manipulation — sunk immunology paper, says author





 After the reviewer of a rejected paper was publicly outed, the BMJ has taken the unusual step of explaining why it chose not to publish the paper.
After the reviewer of a rejected paper was publicly outed, the BMJ has taken the unusual step of explaining why it chose not to publish the paper.

