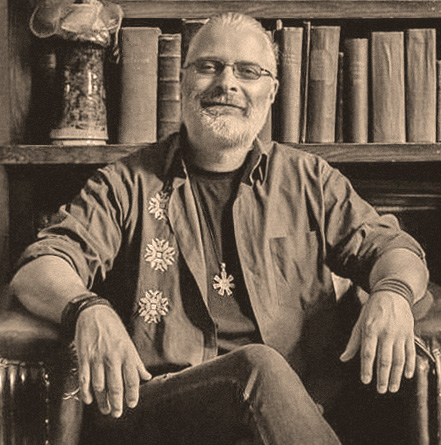
Earlier this year, Milen Zamfirov, dean of the faculty of educational sciences at Sofia University in Bulgaria, was named an exceptional scientist in the social sciences and humanities. As part of the accolades at the prestigious Pythagoras Science Awards from the Bulgarian Ministry of Education and Science, Zamfirov received a commemorative plaque, diploma, and a cash prize of 8,000 BGN (US $4,300).
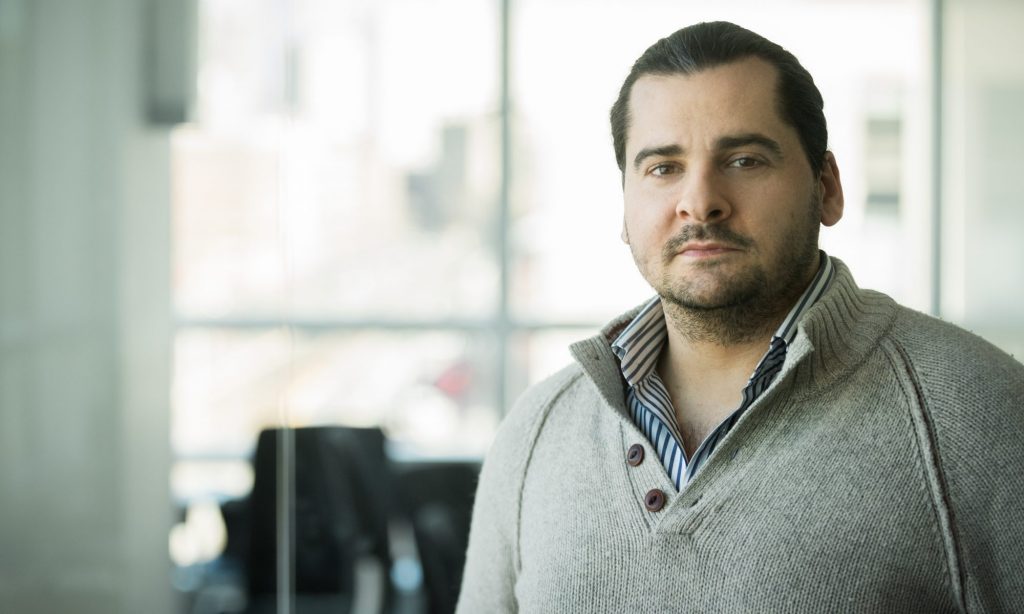
Now, he is accused of plagiarising past research in a paper he co-authored with Margarita Bakracheva, who received a certificate of excellence from the Union of the Bulgarian Scientists earlier this year.
Their study, titled, “In Search of Integrativity of Sciences: the Principle of Supplementarity in the Story of Pauli and Jung,” was published in Bulgarian in 2021.
But the paper seems to have significant overlap with other sources, according to Irene Glendinning, a researcher and consultant based in Leicester, UK.
Continue reading Dean in Bulgaria accused of plagiarism