
The self-proclaimed “father of nutritional immunology,” Ranjit Kumar Chandra, has lost two more papers following the release of a misconduct investigation report by his former employer, Memorial University of Newfoundland (MUN).
The report was released last year after Chandra lost his libel suit against the Canadian Broadcasting Company (CBC). The newly retracted papers were both published in Nutrition Research. On one, the author is listed as “Amrit Jain,” who is allegedly Chandra, as well.
Here’s the retraction notice for the article by Amrit Jain:
Continue reading Nutrition researcher loses two more papers after misconduct findings come to light
 The Leiden University Medical Center (LUMC) has asked a journal to retract two papers after revealing a former employee manipulated data.
The Leiden University Medical Center (LUMC) has asked a journal to retract two papers after revealing a former employee manipulated data.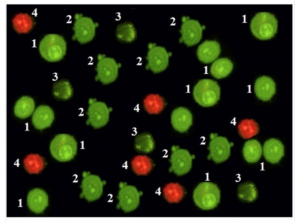


 JAMA has announced it does not intend to retract a 2005 review article about fetal pain, despite requests from anti-abortion activists who claim it has been misused in debates about the procedure.
JAMA has announced it does not intend to retract a 2005 review article about fetal pain, despite requests from anti-abortion activists who claim it has been misused in debates about the procedure.

