 Biologists are retracting three papers after the journal concluded they contain reused images, designed to represent different experiments. The authors stand by the conclusions, some of which they say have been “extensively validated.”
Biologists are retracting three papers after the journal concluded they contain reused images, designed to represent different experiments. The authors stand by the conclusions, some of which they say have been “extensively validated.”
The Journal of Biological Chemistry used image analysis software to evaluate the images, first published at least a decade ago. Unfortunately, the raw data behind the problematic images were not available. The authors have also corrected a fourth paper in another journal, and wrote on PubPeer that they are working with journals to address concerns in three more.
The papers share two authors: Mireia Duñach at the Autonomous University of Barcelona, and Antonio García de Herreros at the Institut Hospital del Mar d’Investigacions Mèdiques. A representative of the Institut Hospital del Mar d’Investigacions Mèdiques told us it is looking into Garcia de Herreros’s work.
We’ll start with “β-Catenin N- and C-terminal tails modulate the coordinated binding of adherens junction proteins to β-catenin,” which has been cited 45 times since it was published in 2002, according to Thomson Reuters Web of Science. The retraction notice says:
Continue reading Authors reused images in three papers, concludes journal probe
 A leading medical journal is taking a second look at a recent high-profile paper about elephants’ lower risk of cancer, after receiving a
A leading medical journal is taking a second look at a recent high-profile paper about elephants’ lower risk of cancer, after receiving a 

 Citation omissions in an economics preprint have set off a wave of recrimination and speculation on a widely read economics discussion board.
Citation omissions in an economics preprint have set off a wave of recrimination and speculation on a widely read economics discussion board.

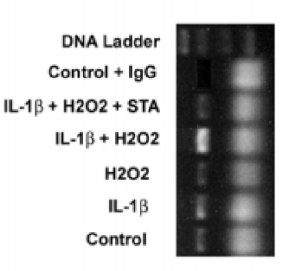
 A major medical journal has updated its instructions to authors,
A major medical journal has updated its instructions to authors,  It was
It was