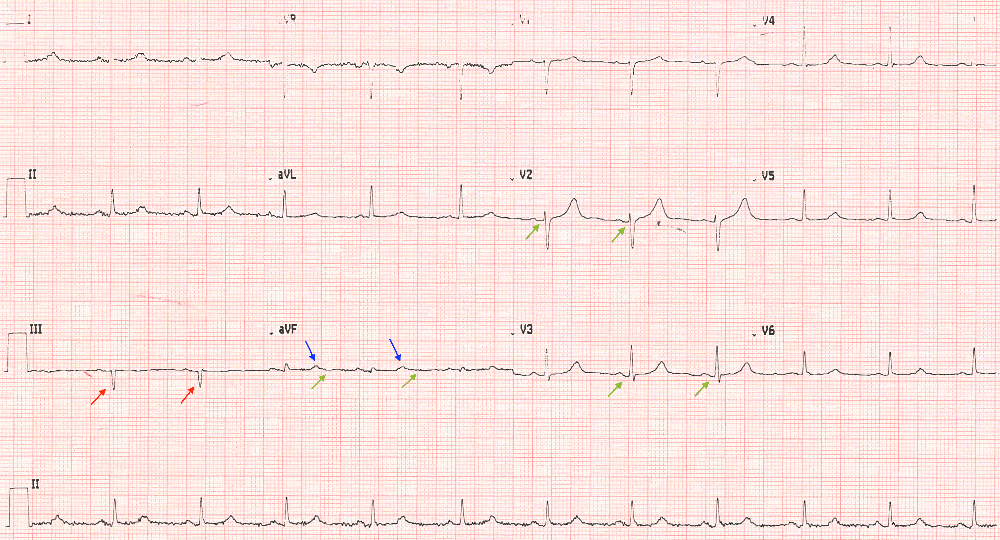
Slovakia’s national science academy has issued a strong critique of a paper on mRNA vaccines coauthored by a member of the country’s parliament. The group called the work “insufficiently detailed” and “lacking controls,” with data that “may be misleading” and conclusions “not supported by sufficiently robust data.”
Peter Kotlár, the paper’s second author, is an orthopedist and represents the far-right Slovak National Party. He is also the commissioner for a review of resource management during the COVID-19 pandemic for the government of populist prime minister Robert Fico, himself known for questioning the science around COVID-19.
The paper appeared May 13 in the Journal of Angiology and Vascular Surgery, published by Herald Scholarly Open Access. “The journal in which the study of Peter Kotlár was published, is not evidenced in databases Web Of Science and Scopus,” a spokesperson for the Slovak Academy of Sciences, Monika Tináková, told us. The issues with the paper reflect “the fact that the journal in which it was published is classified as a so-called predatory journal,” the statement, issued last month, reads.
Continue reading Slovak science academy ‘strictly condemns’ government official’s paper on mRNA vaccines