 A BMJ journal has retracted a medical case report about a couple in the United Kingdom who were infected by parasitic worms while on a Caribbean cruise.
A BMJ journal has retracted a medical case report about a couple in the United Kingdom who were infected by parasitic worms while on a Caribbean cruise.
The paper in BMJ Case Reports included graphic photos of the patients’ buttocks, the site of the infection, which were republished within a week by UK tabloids.
Specifics about when and why the journal retracted the paper remains unclear. BMJ Publishing Group, the journal, and the corresponding author have not responded to multiple requests for comment.
A UK-based lawyer, who has represented doctors in cases that touch on publishing and media law, told us there could be legal trouble. Martin Soames, of London firm Simons Muirhead & Burton, told Retraction Watch that UK laws governing patient confidentiality or protection of personal information could apply, raising problems for both the publisher and the doctors who wrote the paper. [See update at the end of the post, in which the editor says the paper was removed, and “does not consider that there are any issues of liability.”] Continue reading BMJ journal pulls case report after UK tabloids publish graphic photos
 A biology journal is investigating concerns about a 2014 paper by a marine biologist who was found guilty of misconduct last year.
A biology journal is investigating concerns about a 2014 paper by a marine biologist who was found guilty of misconduct last year.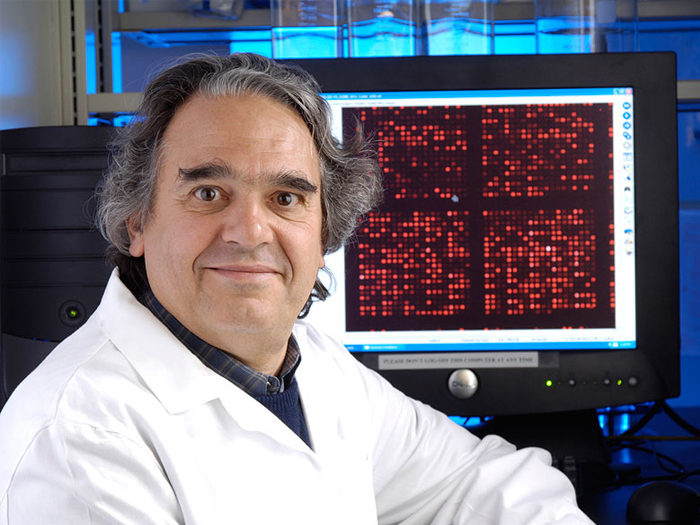

 A chemistry journal has retracted a nanoparticle paper following heavy outcry from readers, who
A chemistry journal has retracted a nanoparticle paper following heavy outcry from readers, who 
 The authors of a highly cited 2016 research letter on a way to improve the efficiency of solar panels have retracted their work following “concerns about the reproducibility.”
The authors of a highly cited 2016 research letter on a way to improve the efficiency of solar panels have retracted their work following “concerns about the reproducibility.”