Dear RW readers, can you spare $25?
The week at Retraction Watch featured:
- University email addresses no longer effective bulwark against fake peer review
- Study on apple cider vinegar for weight loss retracted after many raise concerns
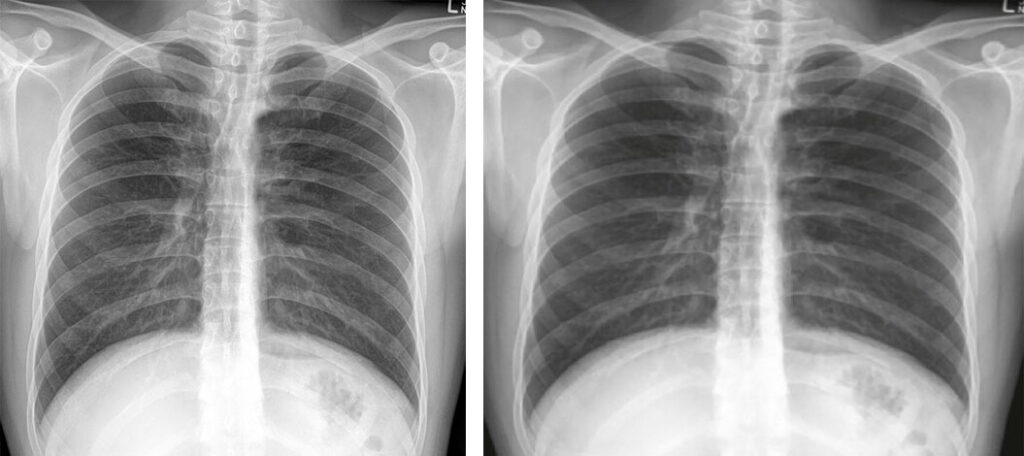
- Second study using ‘Tin Man Syndrome’ X-ray under scrutiny following Retraction Watch inquiry
- Math has publication fraud, too
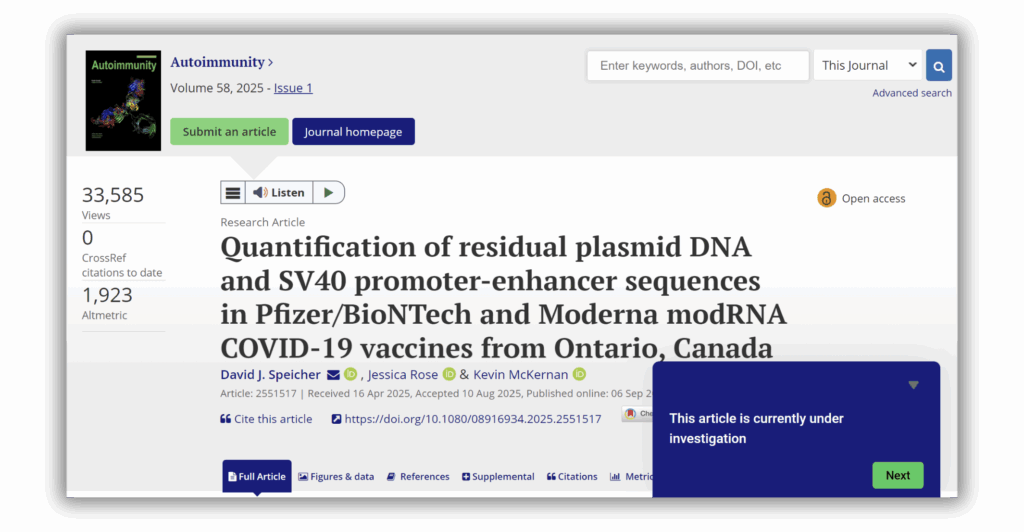
- Authors defend retracted paper on vitamin D and COVID-19 critic called ‘deeply bizarre‘
- Taylor & Francis threatens legal action against anonymous group’s ‘highly defamatory’ claims
Our list of retracted or withdrawn COVID-19 papers is up past 500. There are more than 60,000 retractions in The Retraction Watch Database — which is now part of Crossref. The Retraction Watch Hijacked Journal Checker now contains more than 300 titles. And have you seen our leaderboard of authors with the most retractions lately — or our list of top 10 most highly cited retracted papers? What about The Retraction Watch Mass Resignations List?
Here’s what was happening elsewhere (some of these items may be paywalled, metered access, or require free registration to read):
Continue reading Weekend reads: U.S. EPA tells scientists to stop publishing; ‘unreliable’ Tylenol research; Alzheimer’s paper retracted