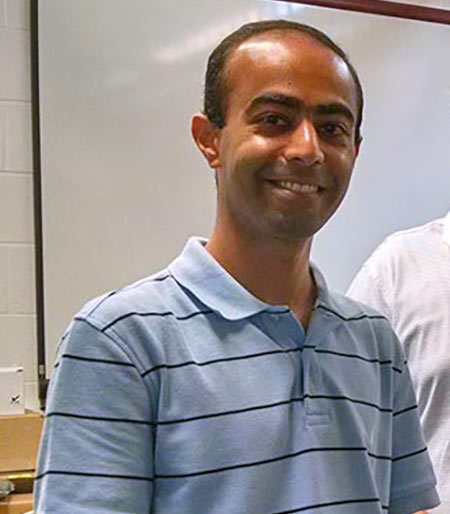

Cornell University and a high-powered dean at the school face being held in contempt of court in a case stemming from their decision to deny tenure to a physics professor.
Assistant professor Mukund Vengalattore told Retraction Watch he believes the school and the dean are violating a judge’s order instructing them to completely redo his tenure review process. Neither the university nor the dean has done any of the things the judge asked them to do, and even suspended his paycheck for the first two weeks of June, he said.
In 2014 Gretchen Ritter, Dean of the College of Arts and Sciences, denied Vengalattore tenure, citing a weak publication record, an inability to accept advice from colleagues, and a poor group dynamic fostered in his lab [Exhibit C in this court document]. But on appeal, a faculty panel found that the review process had been affected by sexual misconduct allegations from a former graduate student. Vengalattore told Retraction Watch the allegations were “completely false.”
However, last year, Ritter again denied Vengalattore tenure, a decision backed by Cornell’s provost, Michael Kotlikoff. As first reported by Inside Higher Ed in May, Vengalattore then took Cornell and Ritter to court. Judge Richard Rich ruled on that case in November, finding that the alleged misconduct “tainted” the process and that the school had deviated from its established procedures in a “necessary” but “secretive” way, denying Vengalattore due process:
 After a
After a 
 The fallout continues for a study conducted at a local CrossFit gym by researchers at The Ohio State University. First
The fallout continues for a study conducted at a local CrossFit gym by researchers at The Ohio State University. First  A former researcher at Johns Hopkins who voiced concerns about a now-retracted paper in
A former researcher at Johns Hopkins who voiced concerns about a now-retracted paper in  A former University of Colorado Boulder graduate student is suing his ex-advisor for defamation after being shooed out midway through his doctoral program.
A former University of Colorado Boulder graduate student is suing his ex-advisor for defamation after being shooed out midway through his doctoral program.  Could a scientific paper ever be considered an advertisement?
Could a scientific paper ever be considered an advertisement? A top federal U.S. court has confirmed a decision by the National Science Foundation (NSF) to
A top federal U.S. court has confirmed a decision by the National Science Foundation (NSF) to  A Federal U.S. court in North Carolina has denied a motion to dismiss a
A Federal U.S. court in North Carolina has denied a motion to dismiss a