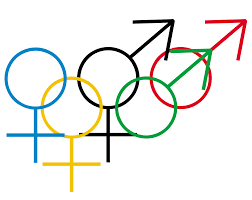 Researcher Floribert Patrick Endong had been looking forward to seeing his paper in print. Several months after he submitted it to Gender Studies, the journal told him in March that it was online. But when he read it, Endong was disappointed to see some changes he had not approved, which he believed “deformed much of the initial text.”
Researcher Floribert Patrick Endong had been looking forward to seeing his paper in print. Several months after he submitted it to Gender Studies, the journal told him in March that it was online. But when he read it, Endong was disappointed to see some changes he had not approved, which he believed “deformed much of the initial text.”
It turns out, the journal “did not allow me to vet the changes before publication,” he explained. Continue reading Author: Journal’s unapproved edits distorted my ideas
 The authors of a highly cited 2016 research letter on a way to improve the efficiency of solar panels have retracted their work following “concerns about the reproducibility.”
The authors of a highly cited 2016 research letter on a way to improve the efficiency of solar panels have retracted their work following “concerns about the reproducibility.” A medical journal has
A medical journal has 




 Title:
Title: