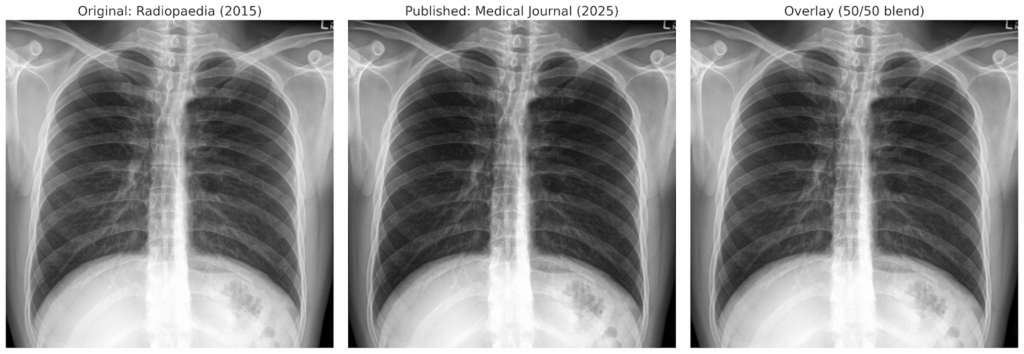
Earlier this year, China’s supreme court said companies selling fake or low-quality research papers should be punished. But shady middlemen there continue to offer questionable deals to journal editors across the globe in a bid to secure publications for their customers, emails obtained by Retraction Watch suggest.
In the emails, sent between May and August and using the same boilerplate language, the Nanjing-based agency A-Techo said it would pay an “expedited processing fee” of $500 to $1,000 US “per accepted manuscript to support the review process.”
According to its website, the company provides various types of publication support. Signatures in the correspondence we obtained listed different names of purported assistant editors, who said they were “writing on behalf of an academic institution that supports Ph.D. researchers and faculty in publishing high-quality research.”
Continue reading ‘Article broker’ in China trying to hook journal editors with fishy publishing deals