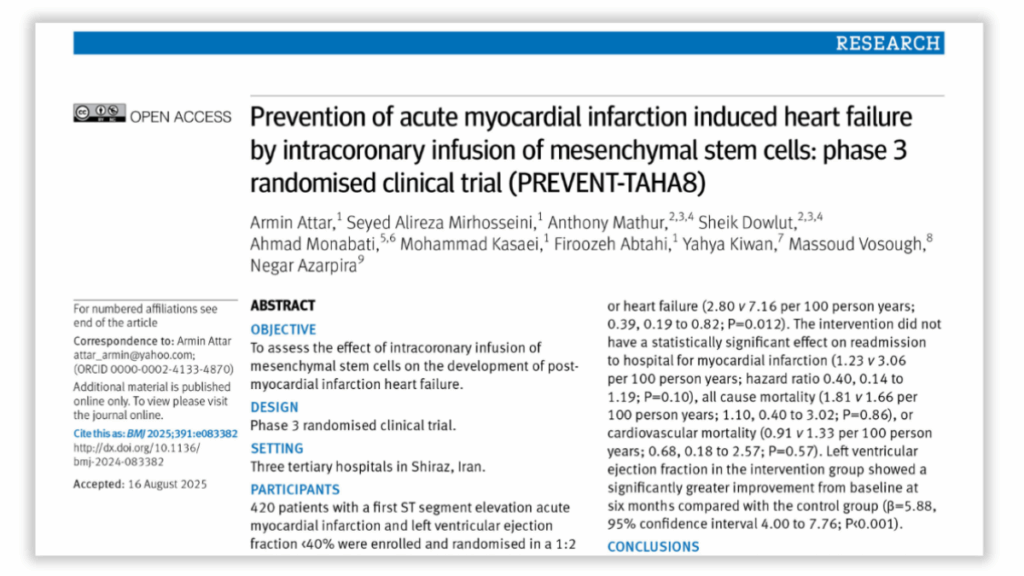
Millions of researchers could be affected by a “dramatic distortion of citation counts” likely caused by flaws in how the academic publishing giant Springer Nature handles article metadata, according to a new preprint.
The bug means a large number of citations are automatically attributed to the first paper in a given journal volume, instead of to whichever paper in that volume they were intended for. The issue appears to affect many of the publisher’s online-only titles, such as Nature Communications, Scientific Reports and several BMC journals.
“It seems that millions of scientists lost a few citations, while tens of thousands, the authors of Article 1s, gained all these, leading to insane citation counts,” Tamás Kriváchy of the Barcelona Institute of Science and Technology, in Spain, told us. His findings appeared earlier this month on arXiv.org. And those citation losses and gains are through no fault (or intention) of the authors themselves. In fact, one author we spoke with has tried, without success, to get mistaken citations removed from her paper.
Continue reading Bug in Springer Nature metadata may be causing ‘significant, systemic’ citation inflation