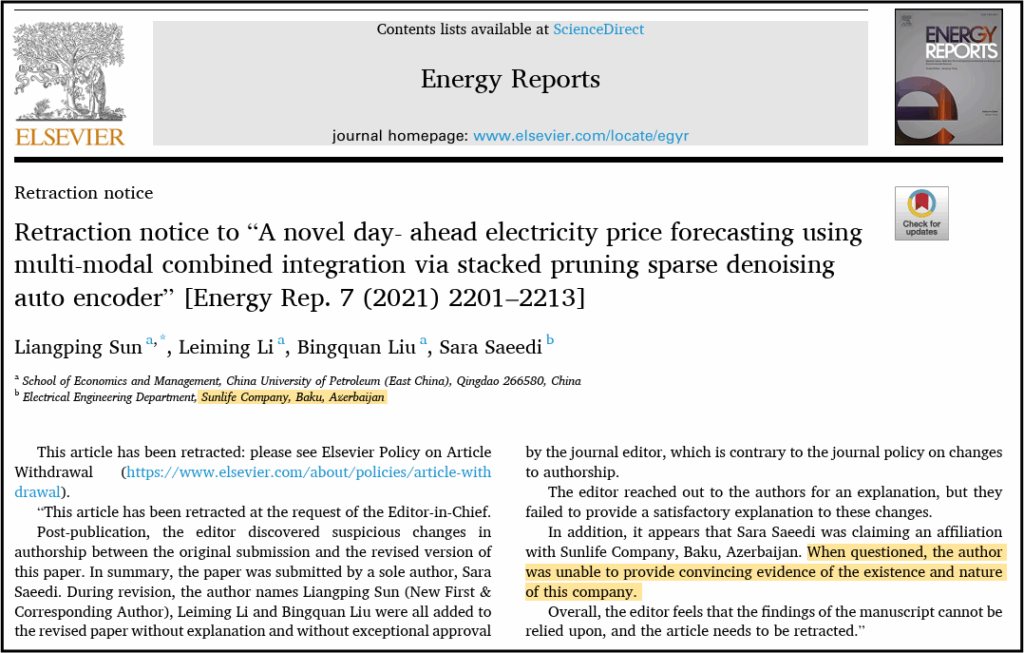
The authors of a paper that went viral with attention-grabbing headlines urging people to throw out their black plastic kitchen tools have corrected the work for a second time.
But a letter accompanying the correction suggests the latest update still fails “to completely correct the math and methodological errors present in the study,” according to Mark Jones, an industrial chemist and consultant who has been following the case. “The errors are sufficient to warrant a restating of the abstract, sections of the paper and conclusions, if not a retraction.”
The paper, “From e-waste to living space: Flame retardants contaminating household items add to concern about plastic recycling,” originally appeared in Chemosphere in September. The study authors, from the advocacy group Toxic-Free Future and the Amsterdam Institute for Life and Environment at Vrije Universiteit Amsterdam, looked for the presence of flame retardants in certain household plastic items, including toys, food service trays and kitchen utensils.
Continue reading Viral paper on black plastic kitchen utensils earns second correction