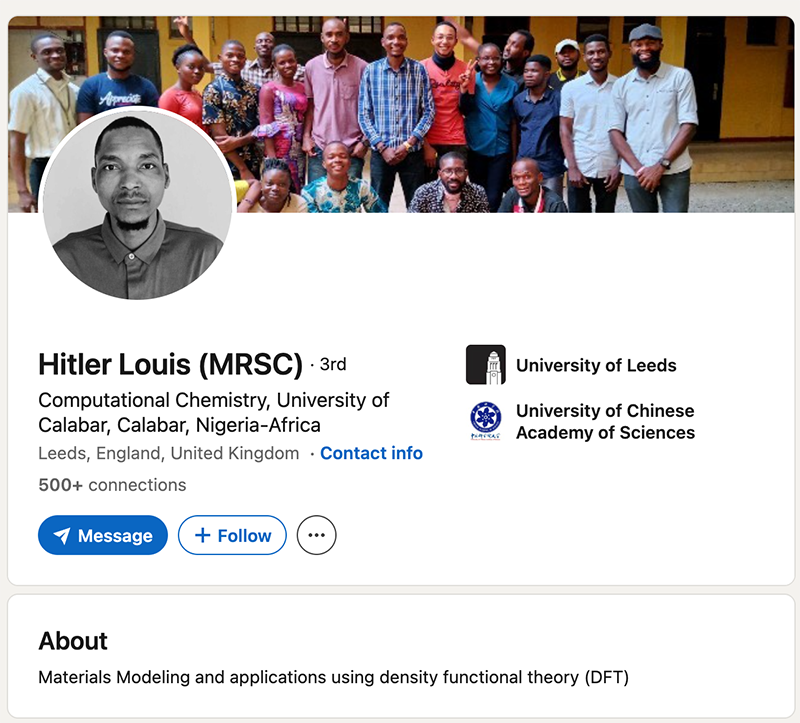
Racking up 35 retractions in just 24 months, chemist Hitler Louis has scored a place on our leaderboard.
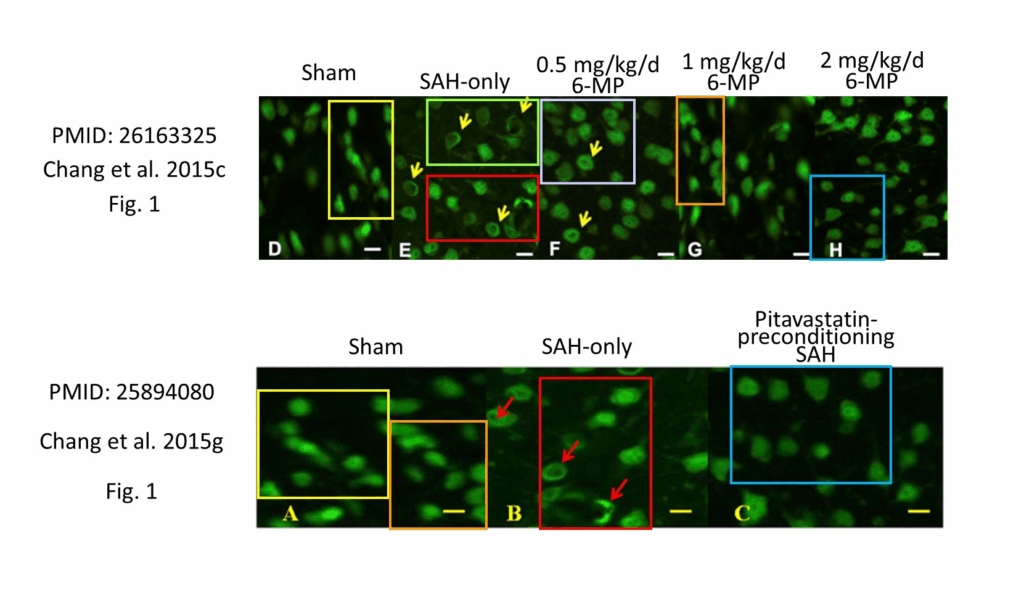
The papers at issue, most of them published in Elsevier and Royal Society of Chemistry journals, exhibit a variety of problems, according to the retraction notices: identical plots supposedly representing different chemical systems, self-citations multiplying between manuscript submission and publication, compromised peer review and fundamental errors in chemical analyses.
Louis – who also goes by Louis Hitler Muzong – did not respond to Retraction Watch’s requests for comment. Until recently, his LinkedIn page named him as a Ph.D. student in computational chemistry at the University of Leeds in the United Kingdom, with an expected completion date of October 2027. But retraction notices for two papers say Louis requested his Leeds affiliation be removed. One states “the research described in the article is not associated with that institution,” and the other that the affiliation “was given incorrectly.” The University of Leeds did not respond to a request to verify whether he was a student there.
Continue reading Chemist nears three dozen retractions for image duplication, self-citation and more